In the previous blog, I covered how memory is being managed when we throw some piece of code into our computer systems. If you have not read about that important concept, you can jump on to this blog and give it a read and if you want to get started with JAVA for the first time then you can hop back to my very first blog of this series.
Flowchart
Every piece of code that we write, follows five key steps that make that program complete. These key steps are also known as flowcharts. A flowchart is a tool to visualize our thought process. It can be used to code even the most complex programs too. It is used by representing with symbols what steps to take to achieve a particular goal. A flowchart has five important steps:
- Start/Stop: The program will start and end. This step is represented by an oval shape.
- Input/Output: The program would take some input and display an output. This step is represented by a parallelogram.
- Processing: The program will process some information while executing. This step is represented by a rectangle.
- Condition: The program will have to make some decisions to achieve a particular goal. This step is represented by the rhombus.
- Flow of direction of the program: This denotes the direction in which the program will execute. This step is symbolized by an arrow.
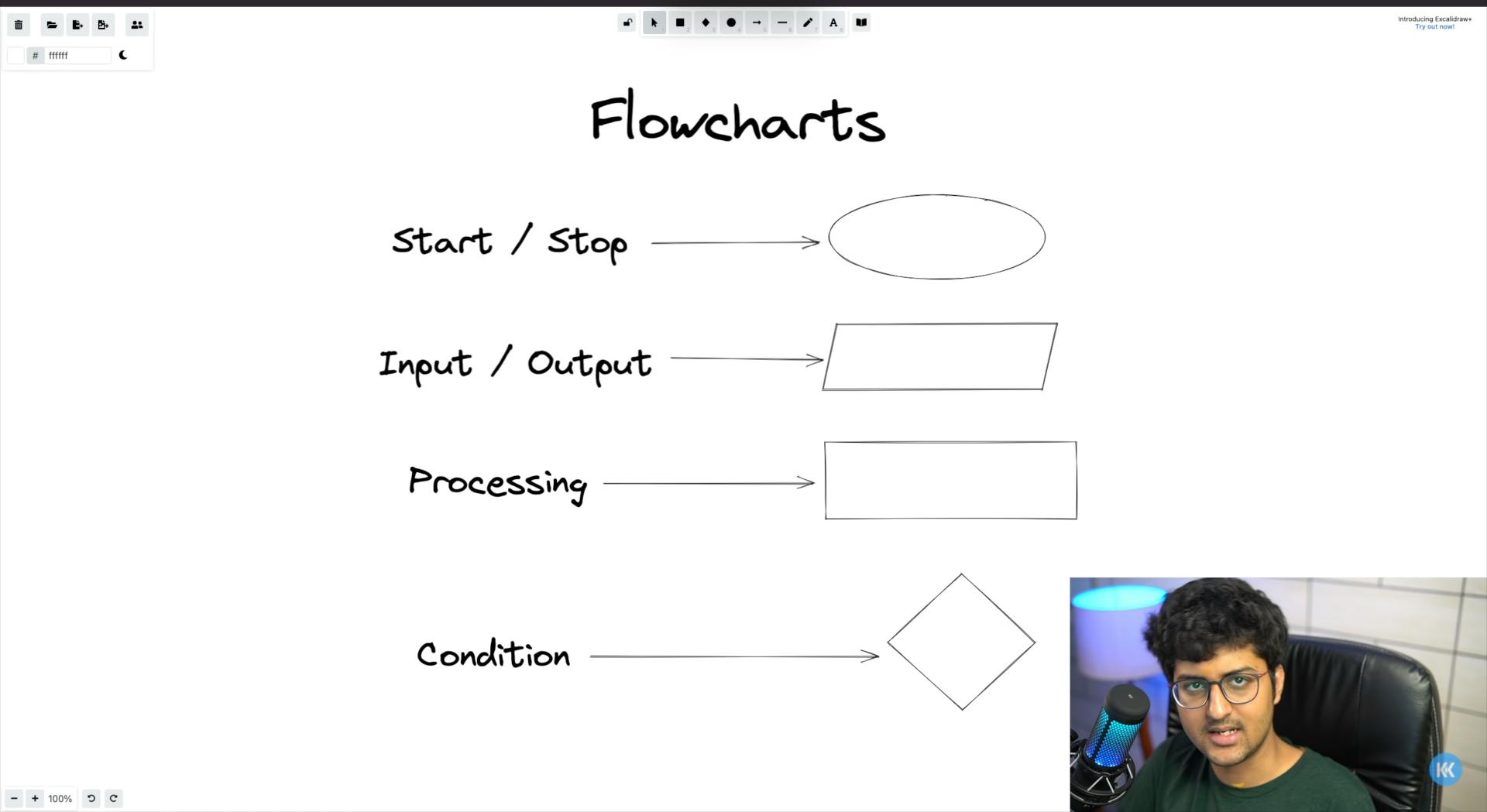
 This is how it looks graphically.
This is how it looks graphically.
To understand this even better, let me explain this to you with the help of an example.
Let's say that we want to take an input "salary" and if the salary is greater than 10,000, we add a bonus of 2000 otherwise we want to add a bound of 1000.
How will we do this in terms of a flowchart?
Well. here's the answer:
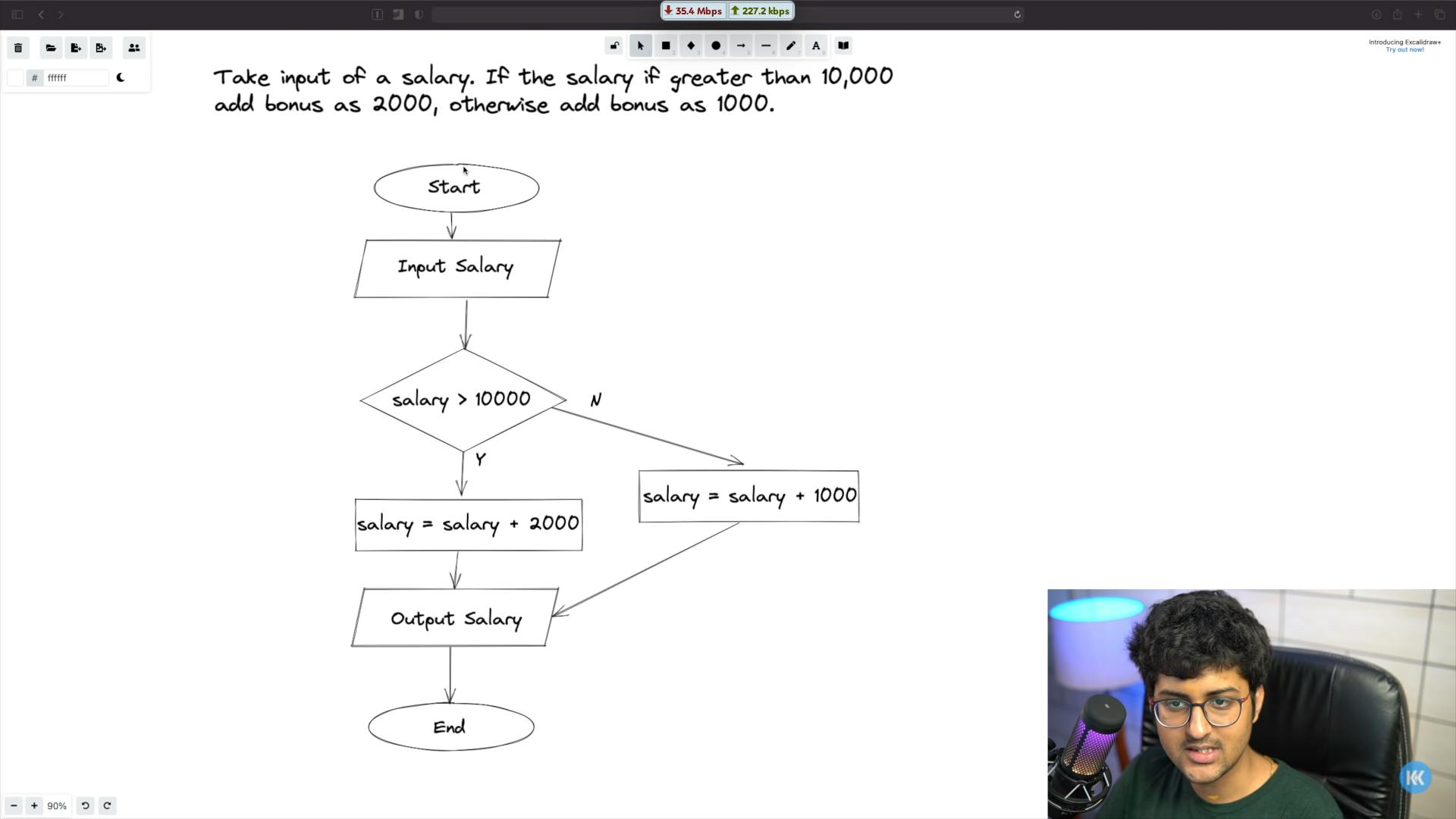
- Our program will start (oval).
- We will take input of salary (parallelogram).
- We will check if the salary is greater than 10,000 which means we will add a condition in our program (rhombus).
- Depending on the fact that if the condition is being satisfied or not, we will add 2000 or 1000 to our salary input which means that we are processing our input here (rectangle).
- After the processing step is complete, we will print the final answer which means that we are displaying an output (parallelogram).
- Once all the required steps are completed, our program will stop (oval).
Pseudocode
A basic but very important concept of computer science is pseudocode. This is another way of representing the steps we need to take to complete a particular task. When we want to share the algorithm (steps involved to complete a task) of our code and don't care much about the syntax during this process of sharing, we only care about explaining what the algorithm for the code is and how it functions, we use pseudocode. Pseudocode can be thought of as a rough code common for all programming languages. This is what the pseudocode for the above example will look like:
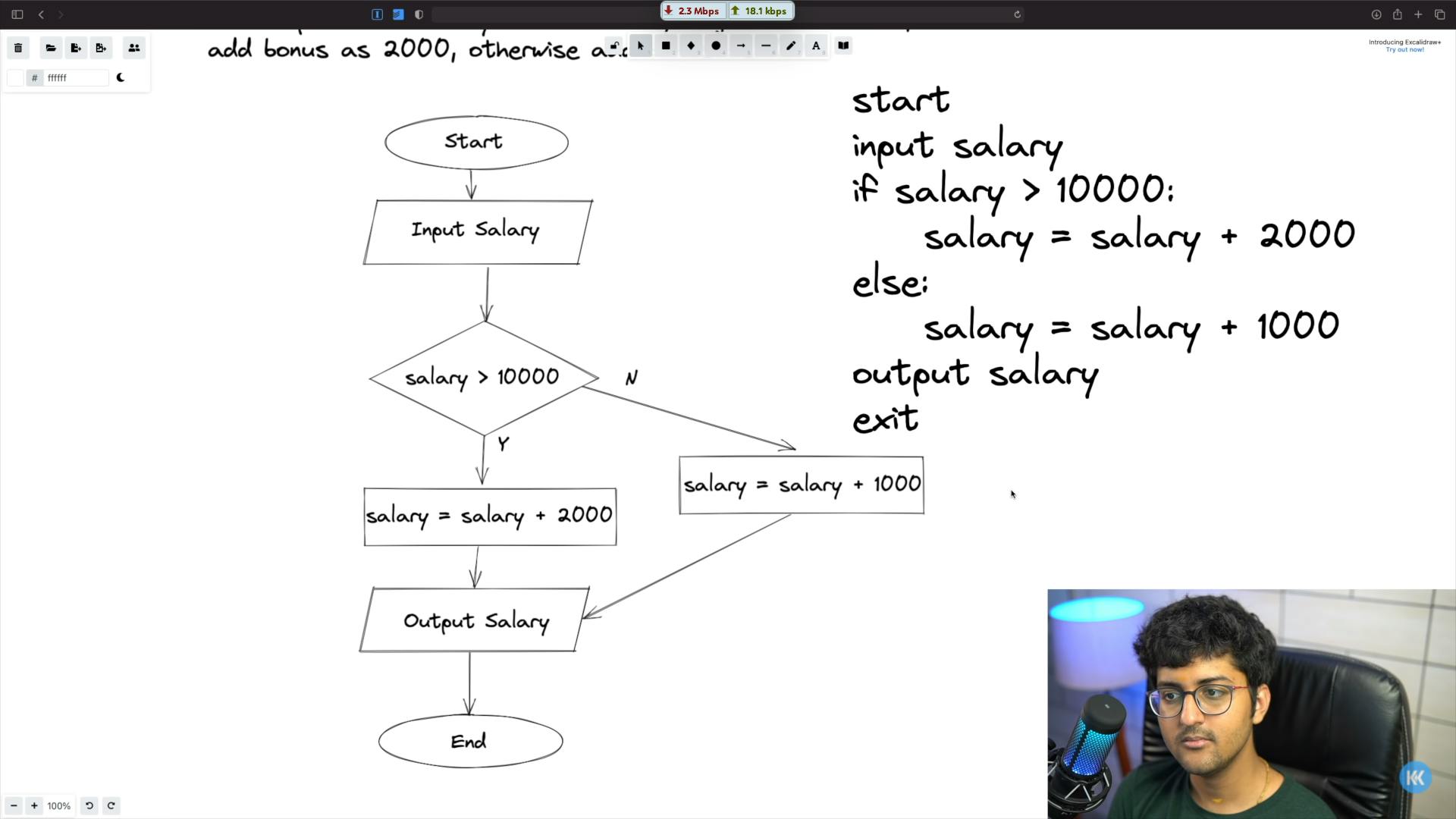
- We start the program.
- We take input.
- We check the condition if the salary is greater than 10,000 using the if (I will cover this later in a separate blog) keyword.
- Next step will be adding the bonus of 2000 to our salary input which will occur inside the if condition only if the condition is satisfied so, we have left a tab space to represent it clearly.
- If the above condition is not satisfied, we use the else keyword to display the alternate steps to take which will occur inside the else condition so we have left a tab space for that too.
- Basically, whatever steps take place inside any condition or loop has to be displayed by leaving a tab space so that it is evident what steps are taking place inside those conditions or loops.
- After the processing part is done we simply output the salary.
- We stop our program.
This was a gist of how the flow of control of a program works and how we can represent the steps we will take to complete the given task via flowchart and via pseudocode. Although I have tried to keep things as simple and detailed as possible but for even more detailed information you can watch this video and you will get a very clear idea of these topics. In the next blog, I will try to cover how a JAVA program executes so, hang on tight!
Let me know comments down below if you like what you read or have some suggestions for me and make sure to follow me on all my social handles to stay connected. Links are on the top-right corner of this page and if you want to get started with JAVA for the first time then you can hop back to my very first blog of this series.
